

TPIA (Third-Party Inspection Agency) empanelment and audit involve certifying independent agencies to assess organizations for regulatory compliance, quality, and safety standards. Empaneled by authorities like the PNGRB, these agencies conduct audits to verify adherence to industry norms, identify non-compliance, and recommend improvements, ensuring transparency and regulatory alignment.

Capacity and Incident Reporting Analysis with Monitoring provides real-time oversight of pipeline performance, tracking flow rates and detecting incidents like leaks or malfunctions. This approach enables quick responses, supports preventive measures, and optimizes resource management, enhancing safety, compliance, and efficiency across the pipeline network for sustainable operations.

An e-Court/e-filing of Board Cases application facilitates the digital submission, management, and tracking of legal cases. It allows users to file documents, access case status, and communicate with relevant authorities securely and efficiently. This system streamlines the legal process, reducing paperwork and ensuring timely updates and compliance.

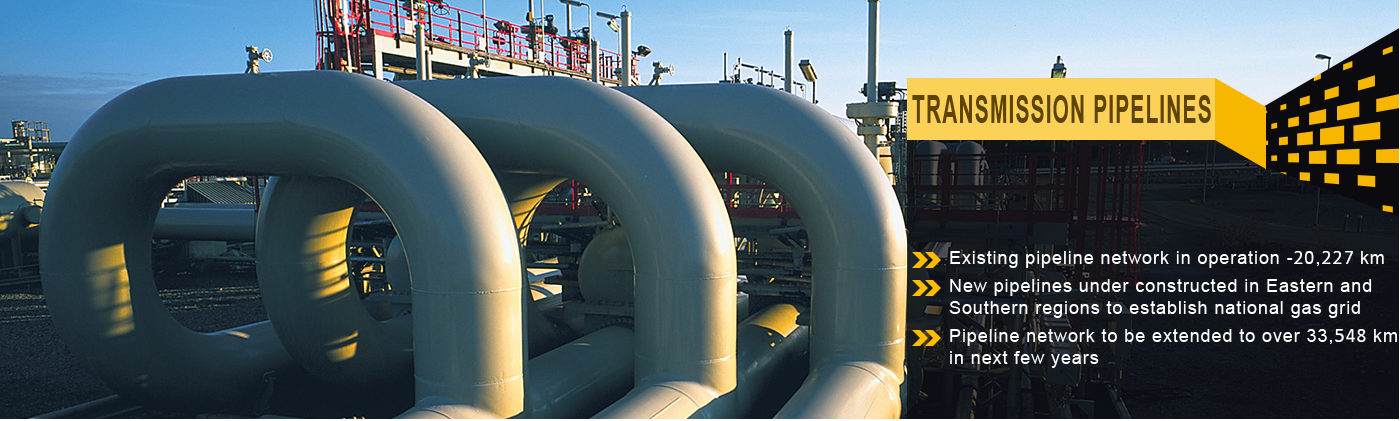
Description: PNGRB is responsible for authorizing and promoting the development of natural gas pipelines across India. This involves assessing applications from companies to construct and operate pipeline networks, as well as facilitating the expansion of the national gas grid. A key element of PNGRB’s infrastructure policy is its open access mandate, which ensures third-party access to existing pipeline infrastructure on a non-discriminatory basis. This promotes competition, equitable access, and optimized resource allocation across the sector.

In the City Gas Distribution (CGD) sector, PNGRB authorizes companies to develop and operate CGD networks, supplying piped natural gas (PNG) to households, industries, and commercial establishments, as well as compressed natural gas (CNG) for vehicles. The board conducts periodic bidding rounds to encourage CGD network expansion, aiming to increase access to clean energy nationwide. PNGRB also monitors operators to ensure they meet quality standards, providing a safe, consistent supply of natural gas to consumers.

PNGRB plays a critical role in setting tariffs for natural gas transportation and CGD services, ensuring fair pricing based on operational costs and efficiency. The board’s transparent tariff structure prevents monopolistic practices by standardizing charges across the sector, balancing consumer affordability with fair returns for operators. PNGRB regularly reviews and adjusts tariffs to align with market dynamics, ensuring stable and accessible pricing for all users.

The PNGRB is dedicated to creating a transparent, competitive marketplace for natural gas and petroleum products. By enforcing open access and fair regulatory policies, PNGRB deters anti-competitive behavior, such as price manipulation or monopolistic control. The board also encourages private sector investment in infrastructure and service provision, fostering innovation, diversification, and enhanced service quality.

Protecting consumers is central to PNGRB’s mission. The board sets high standards for quality of service and provides mechanisms for consumers to lodge complaints and seek redressal for issues related to supply, pricing, and safety. PNGRB also conducts regular inspections and audits to prevent malpractices, ensuring operators adhere to ethical practices that safeguard consumer interests and satisfaction.

PNGRB enforces stringent safety standards for pipeline and CGD operations. These standards cover design, construction, and operational protocols, which are updated regularly to incorporate advancements in technology. The board conducts compliance inspections and audits, and penalties are imposed for non-compliance. PNGRB collaborates with operators to create emergency response plans for incidents like leaks or fires, minimizing public and environmental risks.

The Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) was established in 2006 under the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act. The act aimed to promote competitive markets for petroleum and natural gas, improve infrastructure, and ensure safety and quality. During these initial years, PNGRB focused on laying the groundwork for its regulatory functions, including drafting rules and regulations for the emerging sector.

Between 2008 and 2010, PNGRB started implementing its mandate to regulate the natural gas market. One of its key activities was the creation of a regulatory framework for the construction and operation of gas pipelines and city gas distribution networks. It established guidelines for technical standards and safety protocols, ensuring that companies adhered to safety measures in the transport and distribution of natural gas.

In 2010, PNGRB introduced its first set of tariff regulations, aimed at regulating the transportation costs of natural gas through pipelines. This move was crucial to ensure fair pricing and transparency in the sector. The Board also focused on fostering competition by allowing private players to enter the market, ultimately enhancing the growth of infrastructure and distribution networks.

From 2012 to 2014, PNGRB played a key role in authorizing the development of national and regional natural gas pipelines, as well as city gas distribution (CGD) networks. It issued licenses to companies to establish these critical infrastructures, further promoting the expansion of natural gas in urban and industrial sectors.

In 2015, PNGRB outlined plans for the creation of a National Gas Grid, with the aim of integrating gas transportation infrastructure across the country. This initiative was designed to increase the availability of natural gas to various regions, boosting supply chain efficiency and promoting cleaner energy usage. It supported both economic growth and environmental sustainability by expanding access to natural gas.

During 2016-2017, PNGRB introduced several reforms aimed at increasing consumer protection and market transparency. This included enforcing regulations that ensured consumers received competitive prices for gas. PNGRB also worked on enhancing the transparency of gas pricing by promoting market-based pricing mechanisms.

PNGRB recognized the need for digital transformation in its operations. Between 2017 and 2019, it implemented e-governance systems, which included the development of an e-filing portal for stakeholders to submit applications, track case progress, and submit regulatory filings online. This initiative streamlined operations, improved transparency, and reduced the time required for processing applications.

From 2018 to 2020, PNGRB focused on accelerating the expansion of City Gas Distribution (CGD) networks in multiple cities across India. It issued new licenses for CGD networks, helping to increase the reach of piped natural gas (PNG) to households and compressed natural gas (CNG) to vehicles, thereby promoting cleaner fuel alternatives to traditional sources like LPG and diesel.

Between 2020 and 2022, PNGRB took significant steps to regulate and monitor Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) infrastructure. The Board established regulations for LNG terminals and logistics, ensuring the safe import and distribution of LNG across India. This period also marked a rise in the use of LNG as a cleaner alternative for both domestic and industrial applications, with PNGRB overseeing its integration into the national pipeline network.

In recent years, PNGRB has emphasized sustainability by promoting natural gas as a cleaner energy alternative to coal and oil. Its current focus is on supporting the energy transition by continuing the development of pipeline infrastructure, expanding CGD networks, and monitoring gas usage for both domestic and industrial consumers. As part of future projects, the Board is working on creating a more integrated national pipeline network and facilitating the adoption of renewable energy sources in tandem with natural gas infrastructure.
Shri Anil Kumar Jain has been appointed Chairman of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB). A former Coal Secretary, he brings extensive experience in the energy sector. His role includes overseeing regulations, promoting sustainable practices, and engaging with stakeholders to enhance India's oil and gas infrastructure.
2. Member (Technical)The Member (Technical) is typically an expert in engineering or a related field, with extensive experience in the technical aspects of the petroleum and natural gas sectors. This member’s responsibilities include reviewing technical standards, safety protocols, and ensuring that all gas infrastructure, including pipelines and city gas distribution systems, complies with the prescribed regulations.
3. Member (Finance)The Member (Finance) plays an important role in managing the financial aspects of the Board, including tariff setting, financial regulation of the industry, and ensuring that the economic interests of consumers and stakeholders are considered. This member is typically a person with a strong background in finance, economics, or business management, tasked with overseeing cost recovery mechanisms and financial audits.
4. Member (Legal)The Member (Legal) oversees the legal aspects of the Board's operations, including compliance with the law, the handling of regulatory disputes, and ensuring that the Board’s activities are in line with national and international legal standards. This member is often an expert in legal matters, with a background in regulatory law or energy law.

Shri Anil Kumar Jain was appointed as the Chairman of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) in India. With a strong background in public administration and energy policy, Shri Jain has been instrumental in guiding India's energy and natural gas sector towards sustainable and regulated growth.

Shri Gajendra Singh serves as a Member of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) in India. He brings extensive experience in the oil and gas sector, having held key roles in various public sector organizations related to natural gas infrastructure, supply chain management, and regulatory affairs.

Shri A.K. Tiwari is a member of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) in India. With over 37 years of experience, including a role as Director (Finance) at GAIL, he focuses on regulating the oil and gas sectors, promoting fair practices, and ensuring consumer protection. His expertise is vital for shaping industry policies.

Shri A. Ramana Kumar is a member of the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) in India. He focuses on regulating the petroleum and natural gas sectors, contributing to policy formulation and compliance. His expertise is vital for promoting sustainable practices and enhancing efficiency within the energy sector.